Overcome barriers to healing with a proven iodine dressing
Discover the power of slow-release iodine to provide superior biofilm control and advance healing in acute or chronic wounds. Unlike silver, bacteria shows no known resistance to this iodine dressing in vitro.1, 2, 3, 4 IoPlex provides infection control alone or in combination with other dressings.
Controlled release of iodine
Achieve lasting protection—up to 72 hours—with innovative I-Plexomer® Technology that releases iodine as the dressing absorbs fluids.
Actively manages exudate
I-Plexomer foam efficiently removes exudate from the wound bed surface to help prevent maceration and promote a wound healing environment.
Smart, stackable dressing
Layer IoPlex to increase iodine reserves, manage exudate, and reduce changes. Color fades from black to white when it’s time to change.
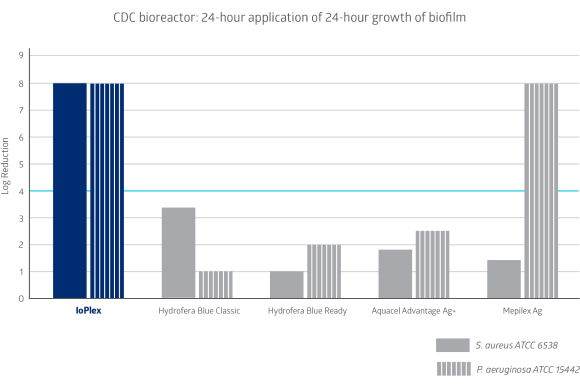
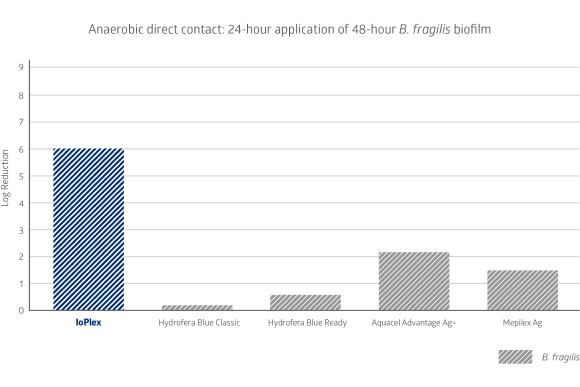
IoPlex outperforms methylene blue and silver dressings
In-vitro testing reveals IoPlex is the only competitive dressing to have a greater than 4 log reduction against S. aureus, P. aureginosa and B. fragilis biofilm strains.5
Click on the charts below to see details enlarged.
Iodine’s superior biofilm control—magnified
The images below show dressings after biofilm exposure at 40x magnification. IoPlex killed more P. aeruginosa biofilm than Hydrofera Blue at 24 hours in vitro.6
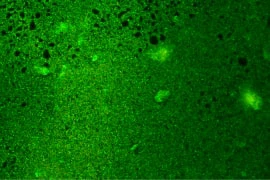
Control: Basic foam dressing
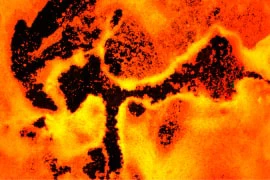
IoPlex
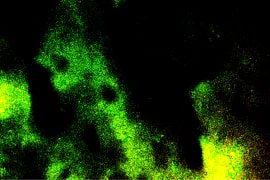
Hydrofera Blue Classic
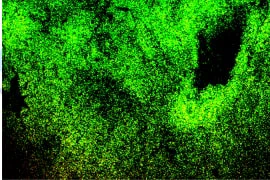
Hydrofera Blue Ready
Experience IoPlex for yourself: Request a sample
Simply complete this form and a Skin Health specialist will contact you soon to coordinate your no-cost sample.

* Indicates required field
See what other clinicians are reading about biofilm management
References:
- Phillips PL, Yang Q, Sampson E, Schultz G. Effects of antimicrobial agents on an in vitro biofilm model of skin wounds. Advances in Wound Care. 2010; 1:299-304.
- Hill KE, Malic S, McKee R, Rennison T, Harding KG, et al. An in vitro model of chronic wound biofilms to test wound dressings and assess antimicrobial susceptibilities. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2010; 65(6):195-206.
- Thorn RMS, Austin AJ, Greenman J, Wilkins JPG, Davis PJ. In vitro comparison of antimicrobial activity of iodine and silver dressings against biofilms. Journal of Wound Care. 2009;18(8):343-346.
- Phillips PL, Yang Q, Davis S, Sampson EM, Azeke JI, et al. Antimicrobial dressing efficacy against mature Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm on porcine skin explants. International Wound Journal. 2015; 12(4):469-483.
- The clinical significance of these findings has not been determined.
- Chen R, Mullin M, Salisbury AM, Percival SL. Evaluation of the Efficacy of an iodine-based wound dressing against biofilms using confocal scanning laser microscopy when in direct contact and when in an artificial wound eschar model. SAWC Spring, 2021.