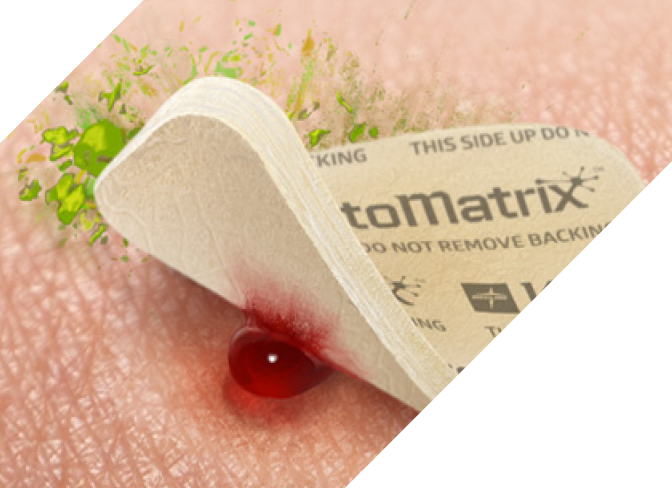
Control the bleed, frontline fast™
Every day, clinicians are under pressure to protect patients from extreme blood loss and achieve hemostasis quickly. KytoMatrix is a unique portfolio of products, specifically designed to control bleeding frontline fast. Powered by chitosan—an organic substance with a positively charged pH that’s especially beneficial in bleeding environments—KytoMatrix helps clinicians overcome their most pressing challenges.
Effective solution for patients on blood thinners
The number of people on blood thinners is up 35%.1 KytoMatrix bleeding control products help prepare clinicians for every situation and patient.
Relieves discomfort when applying pressure
KytoMatrix requires only 5 to 10 minutes of digit pressure—compared to 32 minutes of full pressure for an 8 French access point.2
Helps prevent infection at the site
Chitosan-impregnated KytoMatrix provides an anti-bacterial barrier to 8 different microbes, including MRSA and VRE.3
Treat patients confidently, across the continuum of care
Battlefield-tested and proven industry-wide, KytoMatrix bleeding control products are used by clinicians in a wide range of facilities and units—including interventional radiology (IR), electrophysiology (EP lab), operating room, vascular access, cath lab and the ICU.
KytoMatrix starts working as soon as it’s placed on the wound
The fast-working benefits of chitosan help prepare clinicians for every situation. Here’s how the technology works:
1
Positively charged chitosan attracts the negatively charged red blood cells.
2
The red blood cells rapidly form a clot over the wound.
3
The wound is sealed—and the bleeding is controlled.
Explore the mechanism of action
Click the icons below read more
Take the first step toward faster hemostasis—request a sample
The best way to understand the effectiveness of KytoMatrix dressings is to try one for yourself. Complete this form to learn more about KytoMatrix and request a sample.

References:
1.Barnes, G.D., Lucas, E., Alexander, C., and Goldberger, S.D. National Trends in Ambulatory Oral Anticoagulant Use. The American Journal of Medicine. 2015. 128; 1300-1305.
2.https://cvquality.acc.org/docs/default-source/pci-bleeding-risk-checklist/8-post-pci-sheath-removal-protocolpdf.pdf?sfvrsn=6e5d8dbf_0.
3.Data on file.